Article
The military decoration called the Iron Cross which existed in the Kingdom of Prussia, and later in the German Empire and Third Reich, was established by King Friedrich Wilhelm III of Prussia and first awarded on the 10th of March in 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars. The recommissioned Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War, World War I, and World War II. The Iron Cross was normally a military decoration only, though there were instances of it being awarded to civilians for performing military functions. Two examples of this were civilian test pilots Hanna Reitsch who was awarded the Iron Cross 2nd Class and 1st Class and Melitta Schenk Gräfin von Stauffenberg, who was awarded the Iron Cross 2nd Class, for their actions as pilots during World War II.
The Iron Cross was used as the symbol of the German Army from 1871 to March/April 1918, when it was replaced by the bar cross. The Iron Cross was reintroduced as an award in the Wehrmacht in 1939 with a Swastika added in the center during the Third Reich in World War II. In 1956, the Iron Cross resumed its German military usage, as it became the symbol of the Bundeswehr, the modern German armed forces. The traditional design is black and this design is used on armored vehicles and aircraft. A newer design in blue and silver is used as the emblem in other contexts.
Design
Various iterations from 1813 to 1870
The Iron Cross is a black four-pointed cross with white trim, with the arms widening toward the ends, similar to a cross pattée. Frederick William III commissioned the neoclassical architect Karl Friedrich Schinkel to design the Iron Cross after a royal sketch.[2] It reflects the cross borne by the Teutonic Knights in the 14th century.
The ribbon for the 1813, 1870 and 1914 Iron Cross (2nd Class) was black with two thin white bands, the colors of Prussia. The non-combatant version of this award had the same medal, but the black and white colors on the ribbon were reversed. The ribbon color for the 1939 EKII was black/white/red/white/black.
Since the Iron Cross was issued over several different periods of German history, it was annotated with the year indicating the era in which it was issued. For example, an Iron Cross from World War I bears the year "1914", while the same decoration from World War II is annotated "1939". The reverse of the 1870, 1914 and 1939 series of Iron Crosses have the year "1813" appearing on the lower arm, symbolizing the year the award was created. The 1813 decoration also has the initials "FW" for King Frederick William III, while the next two have a "W" for the respective kaisers, Wilhelm I and Wilhelm II. The final version shows a swastika. There was also the "1957" issue, a replacement medal for holders of the 1939 series which substituted an oakleaf cluster for the banned swastika.
When the Iron Cross was reauthorized for World War I in 1914, it was possible for individuals who had previously been awarded an 1870 Iron Cross to be subsequently awarded another Iron Cross. These recipients were recognized with the award of the 1914 clasp featuring a miniaturized 1914 Iron Cross on a metal bar.[3] It was also possible for a holder of the 1914 Iron Cross to be awarded a second or higher grade of the 1939 Iron Cross. In such cases, a "1939 Clasp" (Spange) would be worn on the original 1914 Iron Cross. (A similar award was made in 1914 but was quite rare, since there were few in service who held the 1870 Iron Cross.) For the 1st Class award, the Spange appears as an eagle with the date "1939" that was pinned above the Cross. Although they are two separate awards, in some cases the holders soldered them together.
A cross has been the symbol of Germany's armed forces (now the Bundeswehr) since 1871.
Early awards
World War I Iron Cross, 2nd Class
Certificate of award to a musketeer in the Royal Prussian Landwehr, October 1918, one month before the end of the War
German soldiers who had been awarded the Iron Cross
On 17 March 1813, Frederick William III – who had fled to the non-occupied Breslau – established the military decoration of the Iron Cross, backdated to 10 March, late Queen Louise's birthday.[4] The Iron Cross was awarded to soldiers during the Wars of Liberation against Napoleon. It was first awarded to Karl August Ferdinand von Borcke on 21 April 1813.[5] King Wilhelm I of Prussia authorized further awards on 19 July 1870, during the Franco-Prussian War. Recipients of the 1870 Iron Cross who were still in service in 1895 were authorized to purchase and wear above the cross a Jubiläumsspange ("Jubilee clip"
The Iron Cross was reauthorized by Emperor Wilhelm II on 5 August 1914, at the start of World War I. During these three periods, the Iron Cross was an award of the Kingdom of Prussia, although given Prussia's pre-eminent place in the German Empire formed in 1871, it tended to be treated as a generic German decoration. The 1813, 1870, and 1914 Iron Crosses had three grades:
Iron Cross 2nd Class (German: Eisernes Kreuz 2. Klasse, or EKII)
Iron Cross 1st Class (German: Eisernes Kreuz 1. Klasse, or EKI)
Grand Cross of the Iron Cross (German: Großkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes, often simply Großkreuz)
Although the medals of each class were identical, the manner in which each was worn differed. Employing a pin or screw posts on the back of the medal, the Iron Cross 1st Class was worn on the left side of the recipient's uniform. The Grand Cross and the Iron Cross 2nd Class were suspended from different ribbons.
The Grand Cross was intended for senior generals of the Prussian or later German Army. An even higher decoration, the Star of the Grand Cross of the Iron Cross (also called the Blücher Star), was awarded only twice, to Generalfeldmarschall Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher in 1813 and to Generalfeldmarschall Paul von Hindenburg in 1918. A third award was planned for the most successful German general during World War II, but was not made after the defeat of Germany in 1945.
The Iron Cross 1st Class and the Iron Cross 2nd Class were awarded without regard to rank. One had to possess the 2nd Class already in order to receive the 1st Class (though in some cases both could be awarded simultaneously). The egalitarian nature of this award contrasted with those of most other German states (and indeed many other European monarchies), where military decorations were awarded based on the rank of the recipient. For example, Bavarian officers received various grades of that Kingdom's Military Merit Order (Militär-Verdienstorden), while enlisted men received various grades of the Military Merit Cross (Militär-Verdienstkreuz). Prussia did have other orders and medals which were awarded on the basis of rank, and even though the Iron Cross was intended to be awarded without regard to rank, officers and NCOs were more likely to receive it than junior enlisted soldiers.
During World War I, approximately 218,000 EKIs, 5,196,000 EKIIs and 13,000 non-combatant EKIIs were awarded. Exact numbers of awards are not known, since the Prussian military archives were destroyed during World War II. The multitude of awards reduced the status and reputation of the decoration. Among the holders of the 1914 Iron Cross 2nd Class and 1st Class was Adolf Hitler, who held the rank of Gefreiter. Hitler can be seen wearing his EKI on his left breast, as was standard, in most photographs.
World War II
The Balkenkreuz of the Wehrmacht during WW II.
Adolf Hitler restored the Iron Cross in 1939 as a German decoration (rather than Prussian), and continued the tradition of issuing it in various classes. Legally, it is based on the enactment (Reichsgesetzblatt I S. 1573[6]) of 1 September 1939 Verordnung über die Erneuerung des Eisernen Kreuzes (Regulation for the Re-introduction of the Iron Cross). The Iron Cross of World War II was divided into three main series of decorations with an intermediate category, the Knight's Cross, instituted between the lowest, the Iron Cross, and the highest, the Grand Cross. The Knight's Cross replaced the Prussian Pour le Mérite or "Blue Max". Hitler did not care for the Pour le Mérite, as it was a Prussian order that could be awarded only to officers. The ribbon of the medal (2nd class and Knight's Cross) was different from the earlier Iron Crosses in that the color red was used in addition to the traditional black and white (black and white were the colors of Prussia, while black, white, and red were the colors of Germany). Hitler also created the War Merit Cross as a replacement for the non-combatant version of the Iron Cross. It also appeared on certain Nazi flags (mostly the Third Reich flags) in the upper left corner. The edges were curved, like most original iron crosses.
Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross
Main article: Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes, often simply Ritterkreuz) recognized extreme battlefield bravery or successful leadership. The Knight's Cross was divided into five degrees:
Knight's Cross (Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes)
Knight's Cross with Oak Leaves (mit Eichenlaub)
Knight's Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords (mit Eichenlaub und Schwertern)
Knight's Cross with Oak Leaves, Swords, and Diamonds (mit Eichenlaub, Schwertern und Brillanten)
Knight's Cross with Golden Oak Leaves, Swords, and Diamonds
In total, 7,313 awards of the Knight's Cross were made. Only 883 received the Oak Leaves; 160 both the Oak Leaves and Swords 27 with Oak Leaves, Swords and Diamonds; and one with the Golden Oak Leaves, Swords,
Previous article:
Wrong History (10 years ago)
About the game:
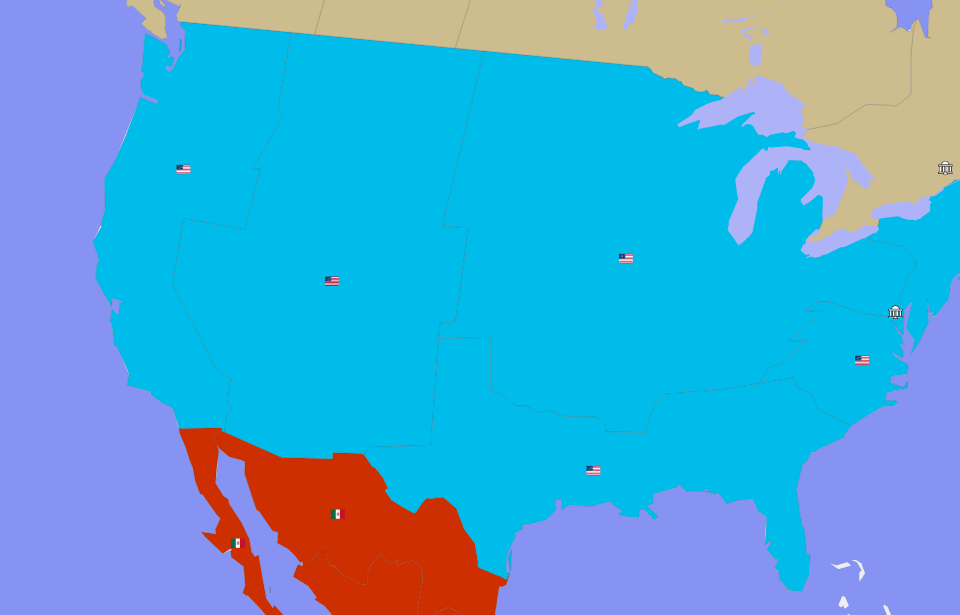
USA as a world power? In E-Sim it is possible!
In E-Sim we have a huge, living world, which is a mirror copy of the Earth. Well, maybe not completely mirrored, because the balance of power in this virtual world looks a bit different than in real life. In E-Sim, USA does not have to be a world superpower, It can be efficiently managed as a much smaller country that has entrepreneurial citizens that support it's foundation. Everything depends on the players themselves and how they decide to shape the political map of the game.
Work for the good of your country and see it rise to an empire.
Activities in this game are divided into several modules. First is the economy as a citizen in a country of your choice you must work to earn money, which you will get to spend for example, on food or purchase of weapons which are critical for your progress as a fighter. You will work in either private companies which are owned by players or government companies which are owned by the state. After progressing in the game you will finally get the opportunity to set up your own business and hire other players. If it prospers, we can even change it into a joint-stock company and enter the stock market and get even more money in this way.
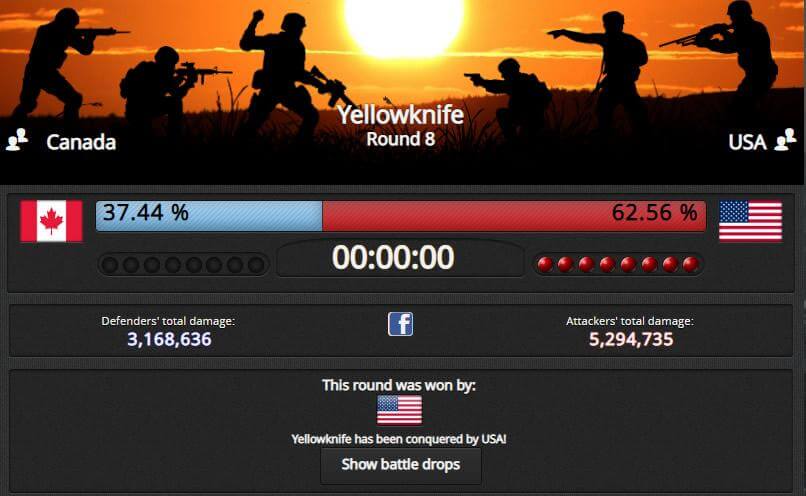
In E-Sim, international wars are nothing out of the ordinary.
Become an influential politician.
The second module is a politics. Just like in real life politics in E-Sim are an extremely powerful tool that can be used for your own purposes. From time to time there are elections in the game in which you will not only vote, but also have the ability to run for the head of the party you're in. You can also apply for congress, where once elected you will be given the right to vote on laws proposed by your fellow congress members or your president and propose laws yourself. Voting on laws is important for your country as it can shape the lives of those around you. You can also try to become the head of a given party, and even take part in presidential elections and decide on the shape of the foreign policy of a given state (for example, who to declare war on). Career in politics is obviously not easy and in order to succeed in it, you have to have a good plan and compete for the votes of voters.
You can go bankrupt or become a rich man while playing the stock market.
The international war.
The last and probably the most important module is military. In E-Sim, countries are constantly fighting each other for control over territories which in return grant them access to more valuable raw materials. For this purpose, they form alliances, they fight international wars, but they also have to deal with, for example, uprisings in conquered countries or civil wars, which may explode on their territory. You can also take part in these clashes, although you are also given the opportunity to lead a life as a pacifist who focuses on other activities in the game (for example, running a successful newspaper or selling products).
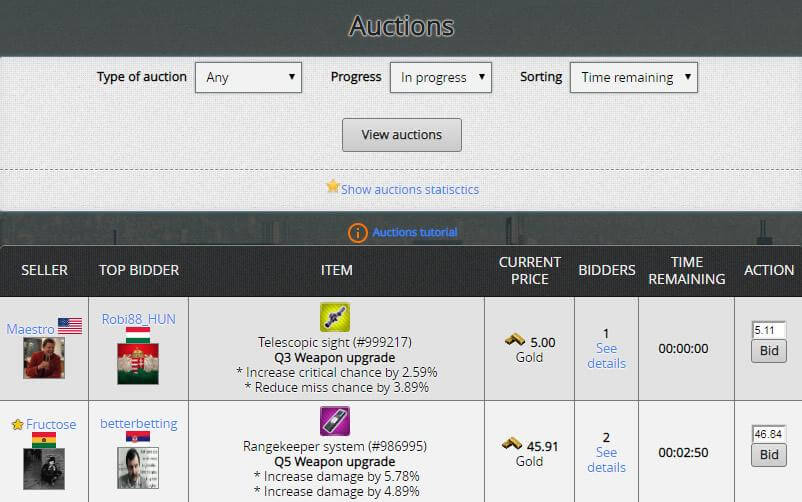
At the auction you can sell or buy your dream inventory.
E-Sim is a unique browser game. It's creators ensured realistic representation of the mechanisms present in the real world and gave all power to the players who shape the image of the virtual Earth according to their own. So come and join them and help your country achieve its full potential.
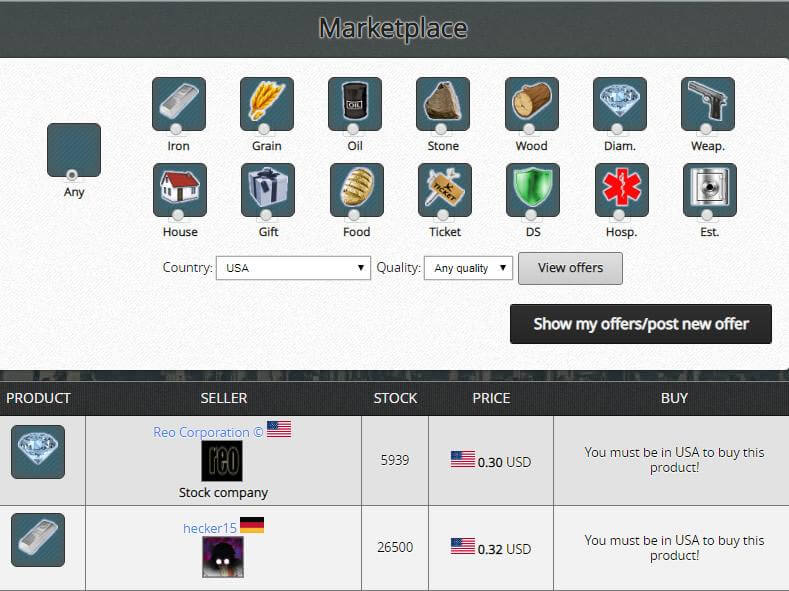
Invest, produce and sell - be an entrepreneur in E-Sim.
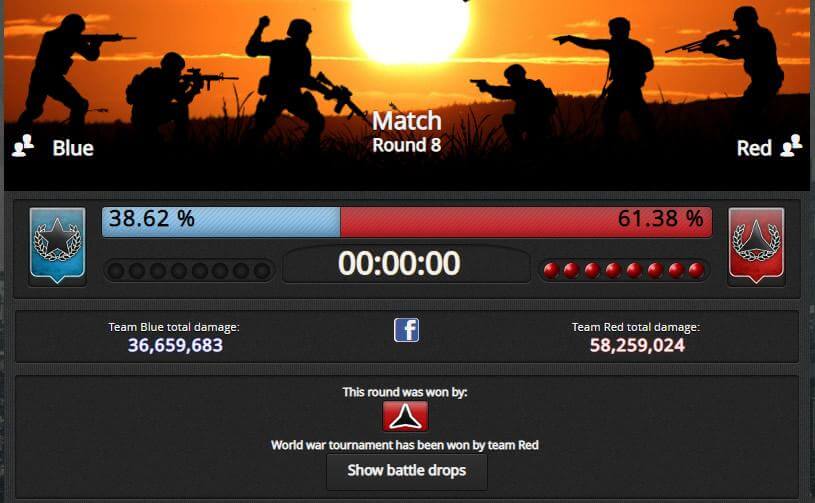
Take part in numerous events for the E-Sim community.
